NEIHPID
North-East India Helminth Parasite Information Database
Recently added
Parasites
Molecular Data
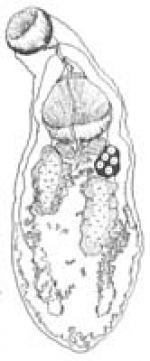
Gorgoderina ellipticum (Dwivedi Dwivedi)
Taxonomy
Platyhelminthes »
TREMATODA »
Digenea »
Gorgoderidae (Looss, 1899) Looss, 1901 »
Gorgoderinae Looss, 1899 »
Gorgoderina Looss, 1902 »
Gorgoderina ellipticum, Dwivedi 1968
Synonyms
(Microlecithus Ozaki, 1926)
Host
Euphlyctis (cyanophlyctis), Limnonectes (limnocharis)
Habitat
Urinary bladder
Locality
Shillong (Meghalaya), Sumer (Meghalaya), Byrnihat (Meghalaya), Khliehriat (Meghalaya), Umkiang (Meghalaya), Smit (Meghalaya), Dimapur (Nagaland)
Description
Body stout, with narrow anterior and tapering posterior end, 1.153-3.41 mm in length, 0.445-1.278 mm in maximum width in immediate post-equatorial region; surface aspinose, thick. Oral sucker completely spherical, terminal in position. Ventral sucker also spherical, conspicuous, larger than oral, situated approximately one-fourth of body length from anterior end. Pharynx absent; oesophagus of moderate length, bifurcating into two intestinal caeca half way between oral and ventral suckers. Caeca long, terminating some distance away from posterior end, placed laterally. Genital organs inter-caecal, post-acetabular. Testes two, oblique, irregularly lobed, situated in middle third of body, one on either side; right testis overlapping caecum, post-ovarian; left testis equatorial, lying opposite ovary. Vesicula seminalis between intestinal bifurcation and ventral sucker transversely placed, S-shaped. Genital pore lying in between intestinal bifurcation and anterior margin of ventral sucker, sub median. Ovary dextral, slightly squarish, equatorial, lobed; oviduct arising from antero-dorsal side of ovary, receiving common vitelline duct from yolk reservoir; Mehlis' gland cells surrounding junction of oviduct, uterus and common vitelline duct. Laurer's canal meeting oviduct in middle. Uterus extensive, filling all available post-acetabular space. Vitellaria compact, smooth, slightly lobed, pear shaped directly posterior to ventral sucker, one on either side of median axis drawn apart, inter-caecal. Eggs small, numerous, oval, 0.025-0.03 x 0.016-0.018 mm.
Remarks
G. ellipticum is the only representative of the genus Gorgoderina from North-East India. Originally the species was described from the same host (= Rana cyanophlyctis) in Madhya Pradesh.Â
The genus Gorgoderina is well represented in amphibians of the Indian subcontinent. Since it is often confused with the closely related genus Phyllodistomum (mainly recorded from salamanders and may occur in frogs), species described under one have been subsequently transferred to the other genus. Baer (1930) described G. carli from an apodan, Uraeotyphlus oxyurus, as a new species from India. Dwivedi (1968) described two more new forms from Madhya Pradesh--G. symmetriorchis from Rana limnocharis and G. infundibulata from Bufo melanostictus. G. guptai Jahan,1973 is probably a renaming of G. indica Gupta et Jahan, 1971- a species reported from Bufo sp. Several forms were originally described in the genus Phyllodistomum. Consequently P. vitelliloba Pande,1937 was synonymised with G. vitelliloba (Olson, 1876) Loss,1902 by Fotedar,(1959) who recorded this species from Bufo virdis and R. cyanophyctis in Kashmir. Further, the forms reported as Phyllodistomum sp. from B. viridis in Kashmir by Kaw (1950) and R. cyanophlyctis in Maharashtra by Mulay and Karyakarte (1973) are considered Gorgorderina species innominata; likewise, P. frequenlatum (sic) Kaw, 1950 is also transferred to Gorgoderina by Prudhoe and Bray (1982).
Helminthological collections record
NEHU/Z - TA/4
Specimen Type
Holotype: W7763/1 in Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata
References
Baer, J. G. (1930) Duex helminthes nouveaux, parasites de Uraeotyphalus oxyurus (Gray), gymnophinoe de l'Inde meridionale. Revue Suisse Zoologie. 37(2):pp 43-52
Dwivedi, M. P. (1968). Three new species of Gorgoderina Looss, 1902. Indian Journal of Helminthology. 19(2):pp 32-172.
Looss, A. (1902). Uber neue und bekannte Trematoden aus Schildkroten, nebst Erorterung zur Systematik und Nomenklatur. Zoologische Jahrbüecher Abteülüng Füer Systematik, Oekoiogie und Geographie Der Tiere. 16(3-6): pp 411-894.
Foteder, D. N.(1959). On a new species of the genus Ganeo Klein. 1905 and some notes on the genus .Journal of Helminthology . 33:pp 151-160.
Kaw, B. L. (1950). Studies in helminthology: helminth parasites of Kashmir. Part. I. Trematoda. Indian Journal of Helminthology. 2(2):pp 67-126.
Mulay, V. B. and Karyakarte, P. P. (1973). Phyllodistomum (Microlecithus) sp. (Trematoda: Gorgoeridae Looss, 1901) from the urinary bladder of the frog, Rana cyanophlyctis in India. Marathwada University Journal of Science. 12 (sci. 5. Biol. Sci.):pp 33-35.
Prudhoe, S. and Bray, R. A. (1982). Platyhelminth parasites of the Amphibia. British Museum (Natural History) and Oxford Press. pp 217.



.jpg)