NEIHPID
North-East India Helminth Parasite Information Database
Recently added
Parasites
Molecular Data
Paramphistomum epiclitum (Fischoeder Fischoeder)
Taxonomy
Platyhelminthes »
TREMATODA »
Digenea »
Paramphistomidae Fischoeder, 1901 »
Paramphistominae Fiscoeder, 1901 »
Paramphistomum Fischoeder, 1901 »
Paramphistomum epiclitum, Fischoeder 1904
Synonyms
(Paramphistomum indicum Stiles et Goldberger, 1910 in part; Paramphistomum thapari Price et McIntosh, 1953; Paramphistomum malayi Lee et Lowe, 1971; Cotylophoron indicum Stiles et Goldberger, 1910; Cotylphoron madrasense Gupta, 1958; Cotylophoron chauhani Gupta et Gupta, 1972; Srivastavaia indica Singh, 1970)
Host
Bos (indicus), Bubalus (bubalis), Capra (hircus), Ovis (aries)
Habitat
Rumen
Locality
Guwahati (Assam), Karimganj (Assam), Moranhat (Assam), Silchar (Assam), Shillong (Meghalaya), Tura (Meghalaya), Nongstoin (Meghalaya), Aizawl (Mizoram), Kohima (Nagaland), Agartala (Tripura)
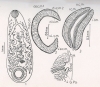
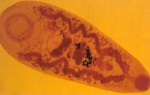
Description
Body elongated, ventrally bent, 6.55-9.71 mm in length, 1.98-3.34 mm in greatest width, ratio of body width to body length 1:2.90-1:4.02. Acetabulum sub-terminal, 1.44-1.80 mm in external diameter, ratio to body length 1:4.53-1:5.56, of paramphistomum type (sensu Näsmark,1937) in median sagittal section; units of dorsal and ventral circular muscles on lateral sides as follows: d.e.c.m. 1. 18-22, d.e.c.m.2. 25-32, d.i.c.m. 30-46, v.e.c.m. 10-14, v.i.c.m. 36-43, m.e.c.m. 20-24. Pharynx 0.63-0.81 mm in length, 0.45-0.81 mm in breadth; ratio to body length 1:10.35-1:12, to diameter of acetabulum 1:2.06-1:2.85; of calicophoron type (sensu Näsmark, 1964) in median sagittal section. Oesophagus 0.45-0.63 mm long, no bulb or posterior sphincter. Caeca in lateral fields, forming few dorso-ventral bends, reaching to level of acetabulum. Testes lobed, tandem; anterior testis 0.81-1.17 mm in length, 0.90-1.62 mm in width; posterior testis 0.83- 1.09 mm in length, 0.90-1.58 mm in width. Seminal vesicle thin walled, coiled; pars musculosa weak; pars prostatica strongly developed. Ovary post-testicular, 0.31-0.45 mm by 0.36-0.49 mm, Mehlis’ gland close to ovary. Laurer's canal crossing excretory vesicle or duct and opening on dorsal surface posterior to excretory pore. Vitellaria in lateral fields, extending from level of oesophagus to middle of acetabulum. Eggs 0.135-0.144 by 0.072-0.089 mm. Terminal genitalium of epiclitum type (sensu Näsmark,1937) in median sagittal section.
Remarks
P. epiclitum has earlier been reported from the Punjab (Gupta, 1963), Calicut in South India (Gupta and Nakhasi, 1977), Andhra Pradesh (Hafeez and Rao, 1978) and Himachal Pradesh (Tandon and Sharma,1981)
The present observations on P. epiclitum tally with those of Näsmark (1937), Gupta (1963) and Eduardo (1982 a,b) except for minor variations in the shape and size of the body and its organs. Slight variation in the number of circular muscle units from that mentioned in the other Indian reports of the species was also observed.
Helminthological collections record
NEHU/Z - TM/4
Specimen Type
Holotype: W7797/1 in Zoological survey of India, Kolkata.
References
Gupta, N. K. (1963) On Pramphistomum epiclitum Fischoeder, 1904, a parasite of the farm animals in Punjab. Research Bulletin (N.S.) of the Panjab University.14:pp 307-311.
Gupta, N. K. and Nakhasi, U. (1977). On some amphistomid parasites from India (Parts I & II). Revista Iberica de Parasitologia. 37:pp 205-225, 252-272.
Hafeez, Md. and Rao, B. V. (1978). Studies on amphistomes and amphistomiasis of sheep and goats in Andhra Pradesh. Journal of Research, Andhra Pradesh Agricultural University. 5:pp 1-5.
Tandon ,V. and Sharma, V. (1981). Amphistome fauna of ruminants in Himachal Pradesh. Indian Journal of Parasitology .5:pp 241-245.
Näsmark, K. E. (1937) Revision of the trematode family Paramphistomidae. Zoologiska Bidrag fran Uppsala. 16:pp 301-565.
Eduardo , S .L. (1982a) The taxonomy of the family Paramphistomidae Fischoeder, 1901 with special reference to the morphology of species occurring ruminants. I. General consideration. Systematic Parasitology. 4:pp 7-57.
Eduardo , S .L. (1982b). The taxonomy of the family Paramphistomidae Fischoeder, 1901 with special reference to the morphology of species occurring ruminants. II. Revision of the genus Paramphistomum Fischeoder, 1901. Systematic Parasitology. 4:pp 189-238.